Oxygen Therapy
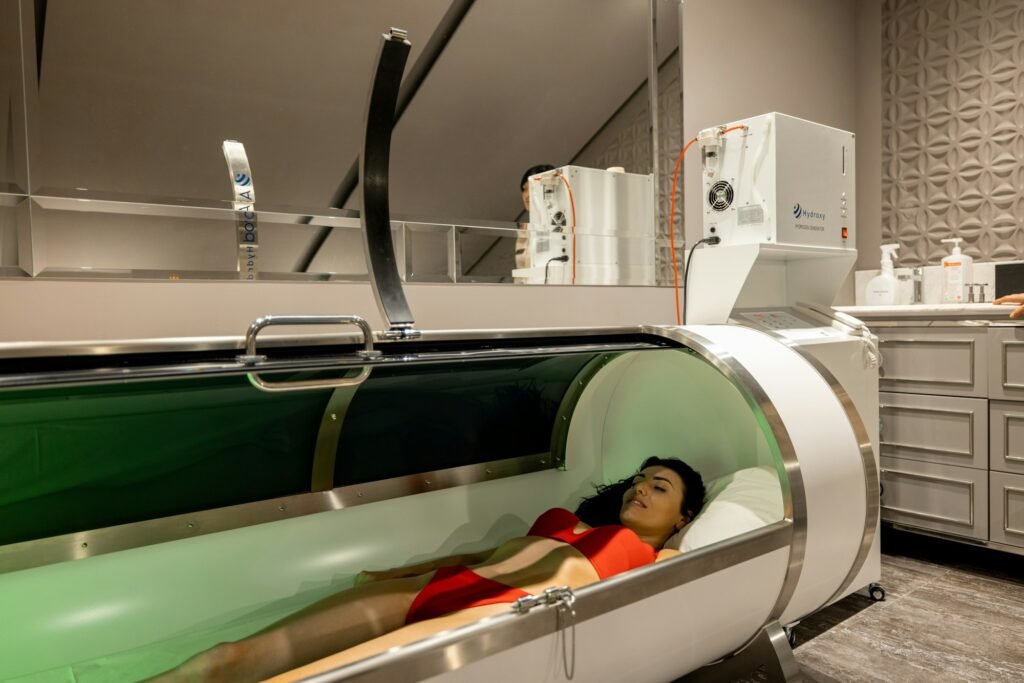
Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen Therapy is a therapeutic modality that goes beyond the vital oxygen we breathe daily. It involves utilizing various methods of increasing oxygen availability to the body for promoting healing and improving overall health and well-being.
What is Oxygen Therapy?
Oxygen Therapy encompasses several key forms:
- Supplemental Oxygen: Delivery of oxygen via nasal cannula, masks, or other devices for those who can’t get enough on their own.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Administration of 100% pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, allowing higher levels to dissolve in the blood.
- Other Emerging Methods: Exploration of modalities like ozone therapy or exercises with controlled oxygen levels for potential benefits.
How Can Oxygen Therapy Help You?
Oxygen Therapy provides support in the following ways:
- Addressing Respiratory Conditions: Often used for COPD, asthma, pneumonia, or other conditions affecting efficient oxygen uptake.
- Wound Healing: Promotes oxygen delivery to injured tissues, aiding in recovery from burns, diabetic ulcers, etc.
- Decompression Sickness: HBOT is a vital treatment for the ‘bends’ experienced by divers ascending too quickly.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: May enhance healing and reduce infection risk by increasing oxygenation at the cellular level.
What is Oxygen Therapy Good For?
Oxygen Therapy is especially beneficial for those with:
- Chronic Lung Conditions: Helping manage symptoms and improve breathing capacity in disorders where oxygen levels are compromised.
- Difficult-To-Heal Wounds: Oxygen can offer a significant boost when traditional wound care isn’t progressing as needed.
- Certain Infections: HBOT may be beneficial for severe infections, particularly those involving oxygen-sensitive bacteria.
- Performance & Recovery: Exploratory use in athletes for potential enhancements in performance or quicker post-exercise recovery.
Benefits of Oxygen Therapy
- Enhanced Tissue Oxygenation: Fights hypoxia (low oxygen) at the cellular level, supporting essential metabolic processes.
- Accelerated Healing: Improved oxygen delivery helps the body repair damaged tissues more efficiently.
- Reduced Inflammation: Can have anti-inflammatory effects, beneficial for various conditions and aiding in recovery.
- Potential for Improved Brain Function: Some studies suggest HBOT could have neuroprotective effects after brain injuries.
What to Expect with Oxygen Therapy
- Forms of Delivery: Varies depending on the type. Simple nasal cannulas, masks, or HBOT chambers with pressurization.
- Consultation: Your doctor determines if Oxygen Therapy is appropriate and prescribes the dosage, duration, and delivery method.
- Supervision: Typically administered in hospitals, clinics, or certified HBOT centers with trained personnel monitoring.
- Adjunctive Therapy: Often used alongside other treatments, not as a stand-alone solution for underlying conditions.
Similar Modalities to Oxygen Therapy
- Acupuncture: May indirectly improve oxygenation by stimulating circulation and promoting overall respiratory function.
- Biofeedback: Techniques teaching breath control may improve lung capacity and optimize oxygen intake.
- Breathwork Techniques: Specific breathing exercises may enhance respiratory function and oxygen utilization.
Final Thoughts
Oxygen Therapy can be a valuable tool in addressing various health challenges, particularly where lack of oxygen hampers healing or well-being. While Oxygen Therapy is primarily utilized within a medical treatment context, research exploring its potential for broader uses in wellness and athletic performance is ongoing.
Scientific References
- Gill, A. L., & Bell, C. N. (2004). Hyperbaric oxygen: its uses, mechanisms of action and outcomes. QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, 97(7), 385-395. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hch074
- Mathieu, D., Linke, J. C., & Wattel, F. (Eds.). (2006). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Best Publishing Company. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4448-8_20
- Thom, S. R. (2011). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for acute carbon monoxide poisoning. New England Journal of Medicine, 364(6), 555-556. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa013121
Recommended Reading
- Oxygen: The Molecule That Made the World by Nick Lane
- The Oxygen Advantage by Patrick McKeown (focused on breathing techniques)
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy by Richard Neubauer & Selim Unver (for in-depth clinical perspective)
FAQ: Oxygen Therapy
Is Oxygen Therapy safe?
When administered correctly, it’s generally safe. However, potential risks exist, like oxygen toxicity in extreme doses or fire hazard with HBOT.
Can I get Oxygen Therapy at home?
Home oxygen may be prescribed for chronic conditions. Follow safety guidelines strictly, as oxygen is flammable.
Does Oxygen Therapy cure my condition?
It’s usually supportive, not curative. It may significantly improve symptoms and healing but often needs to be combined with treatments addressing the cause.
Is Oxygen Therapy considered holistic?
It overlaps with holistic care when viewed as supporting the body’s natural healing abilities, but may be used alongside conventional medicine.
How will I know if Oxygen Therapy is working for me?
Improvements may be seen in wound healing rates, reduced shortness of breath, better energy, or specific test results ordered by your doctor.
Related Practitioners
Kim McIntire
The Neurodivergent Healer & Hypnotist
- Carson City, Nevada, United States
- +1 (775) 240-6381
My name is Kim McIntire, and my transformative journey in holistic wellness commenced 22 years ago during my time at… Read More
Ali Campbell
Neuro Linguistic Programming Expert
- Los Angeles, Los Angeles County, California, United States
- +44 (2) 555-5555
As information is rapidly changing, we encourage you to continue to stay informed. Please visit our Coronavirus Resource Center, Healthgrades… Read More
Kamela Hurley
Manifest Miracles with Kamela Hurley Medium + Holistic Wellness Coach
- Old Toronto, Toronto, Golden Horseshoe, Ontario, Canada
Throughout my spiritual journey, I have found a profound connection to the natural surroundings that encompass me. It has been… Read More





















